Java对象内存布局和对象头
先从面试题说起

Object object = new Object()
谈谈你对这句话的理解?一般而言JDK8按照默认情况下,new一个对象占多少内存空间
构成布局
可以联想一下我们的HTML报文

对象在堆内存中布局
在HotSpot虚拟机里,对象在堆内存中的存储布局可以划分为三个部分:
对象头
实例数据
对齐填充

下面分别是 java对象 和数组(数组对象会多一个length),原理其实类似
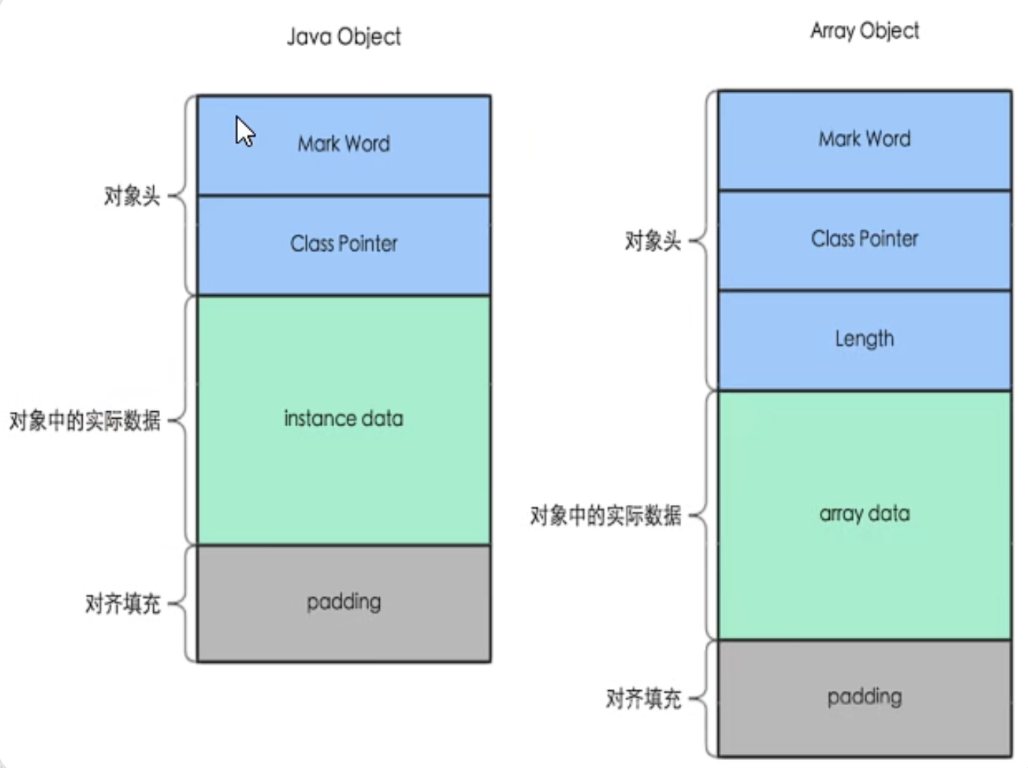
1.对象头
- 对象头分为**对象标记(markOpp)**和 类元信息 (klassOop)
- 类元信息存储的是指向该对象类元数据(klass)的首地址。
先提出几个问题来引出下面的概念
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = new Object();//?new 一个对象,内存占多少,记录在哪里?
System.out.println(o.hashCode());//356573597,这个hashCode又是记录在哪里的
synchronized (o){//加锁信息又是记录在哪里的
}
System.gc();//手动垃圾收集中,15次可以从新生代到养老区,那这个次数又是记录在哪里的
}
}public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = new Object();//?new 一个对象,内存占多少,记录在哪里?
System.out.println(o.hashCode());//356573597,这个hashCode又是记录在哪里的
synchronized (o){//加锁信息又是记录在哪里的
}
System.gc();//手动垃圾收集中,15次可以从新生代到养老区,那这个次数又是记录在哪里的
}
}- 刚刚几个问题都保存在对象标记里
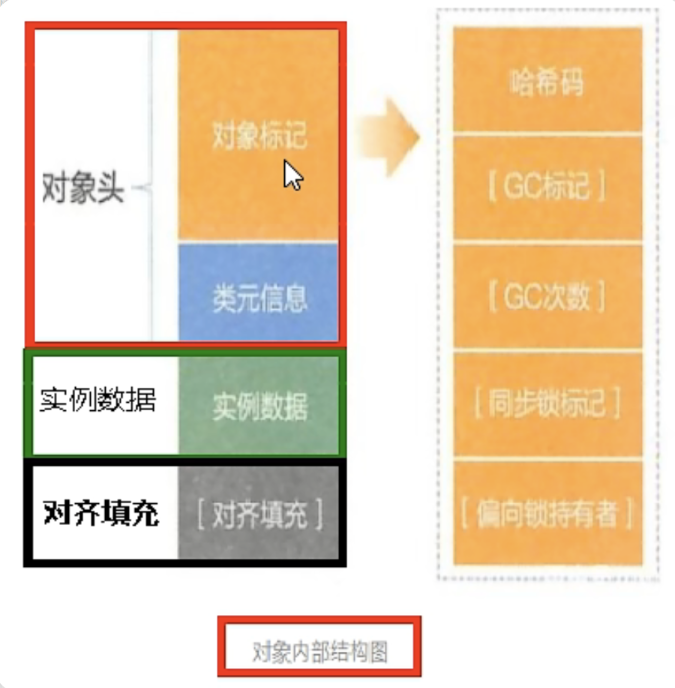
- 对象标记Mark Word
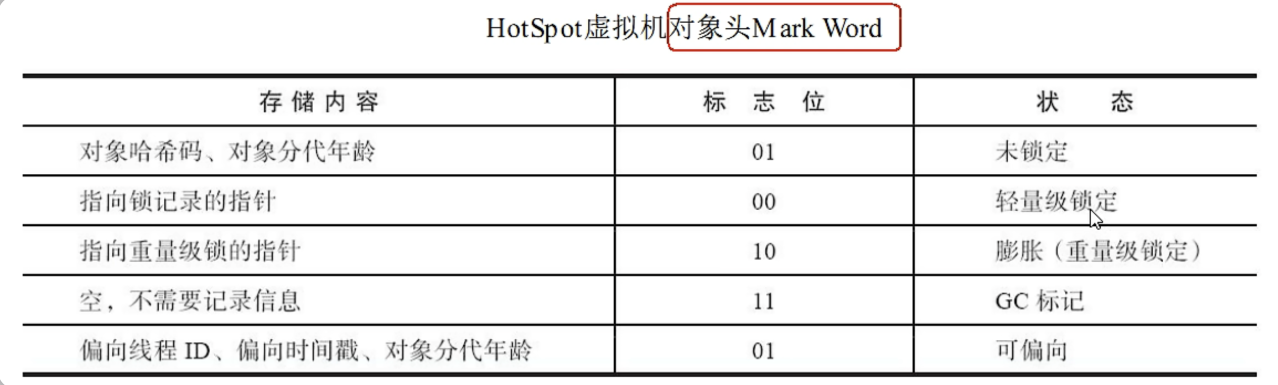
- 在64位系统中,MarkWord占了8个字节,类型指针占了8个字节,一共是16个字节

默认存储对象的HashCode、分代年龄和锁标志位等信息。这些信息都是与对象自身定这无关的数据,所以MarkWord被设计成一个非固定的数据结构以便在极小的空间内存存储尽量多的数据。它会根据对象的状态复用自己的存储空间,也就是说在运行期间MarkWord上存储的数据会随着锁标志位的变化而变化。
- 类元信息(又叫类型指针)Class Pointer
所谓的类元信息(类型指针)其实就可以说是模板
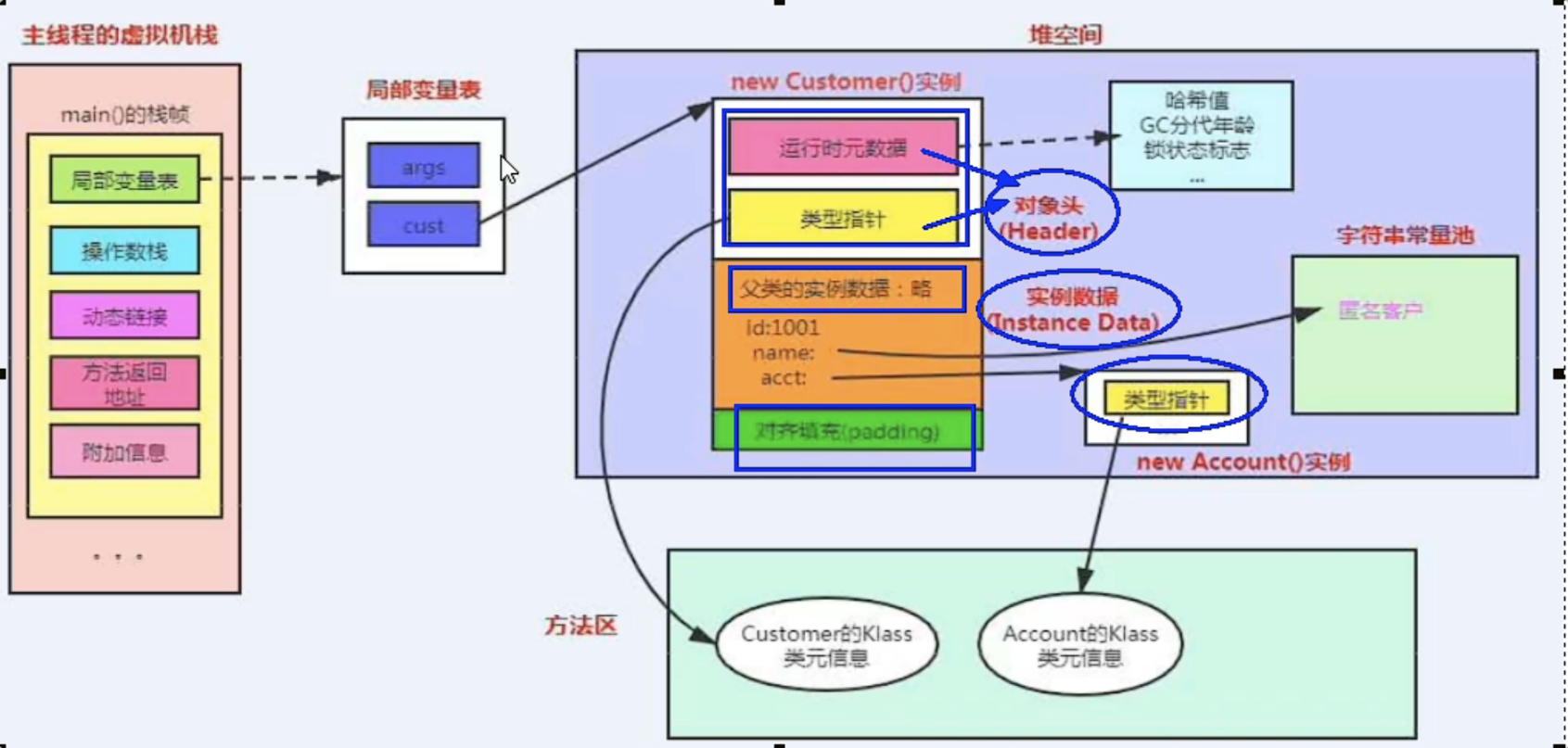
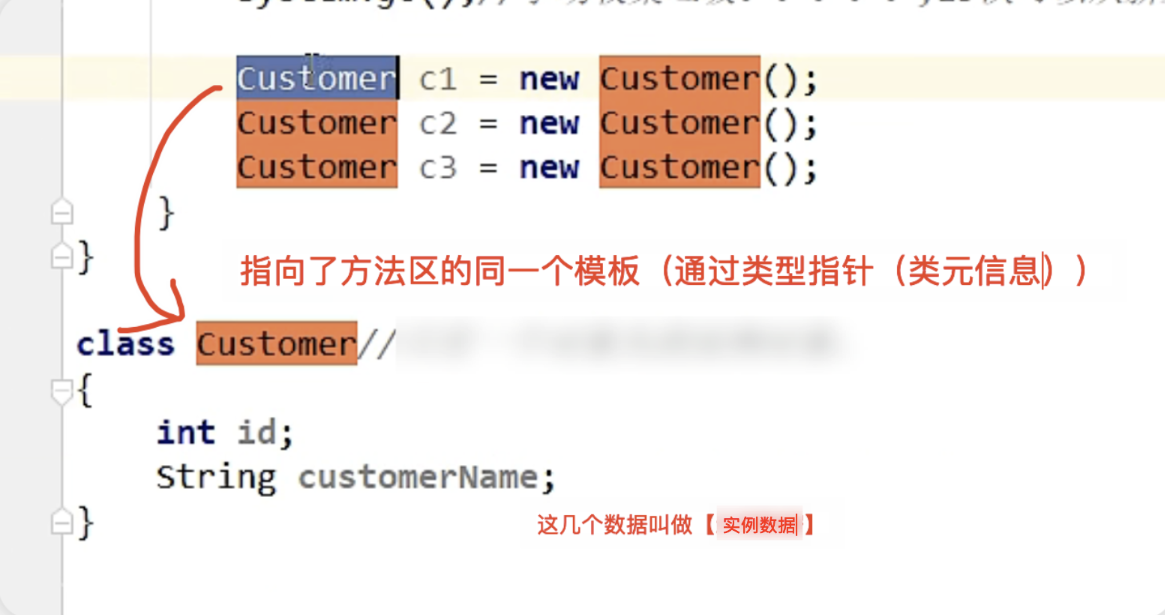
- 对象指向它的类元数据的指针,虚拟机通过这个指针来确定这个对象是哪个类的示例。
对象头有多大?
- 在64位系统中,MarkWord占了8个字节,类型指针占了8个字节,一共是16个字节
2.实例数据
实例数据:存放类的属性(Field)信息,包括父类的属性信息

3.对齐填充
用来保证8字节的倍数
对齐填充:虚拟机要求对象起始地址必须是8字节的整数倍。填充数据不是必须存在的,仅仅是为了字节对齐这部分内存按8字节补充对齐。
有个案例,对象头16+实例数据5+对齐填充3=24字节

官网理论
- Hotspor术语表官网
http://openjdk.java.net/groups/hotspot/docs/HotSpotGlossary.html

- 底层源码理论证明
http://hg.openjdk.java.netjidlk8u/jdk8u/hotspot/file/89fb452b3688/src/share/vm/oops/oop.hpp
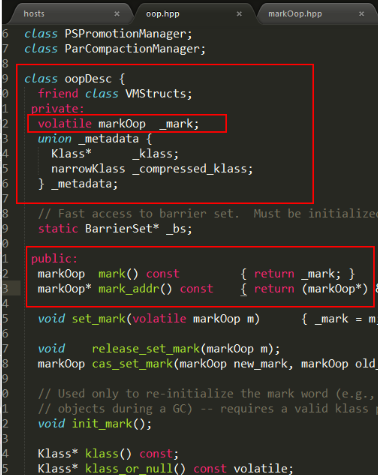
mark字段是mark word, metadata是类指针klass pointer, 对象头(object header)即是由这两个字段组成,这些术语可以参考Hotspot术语表,

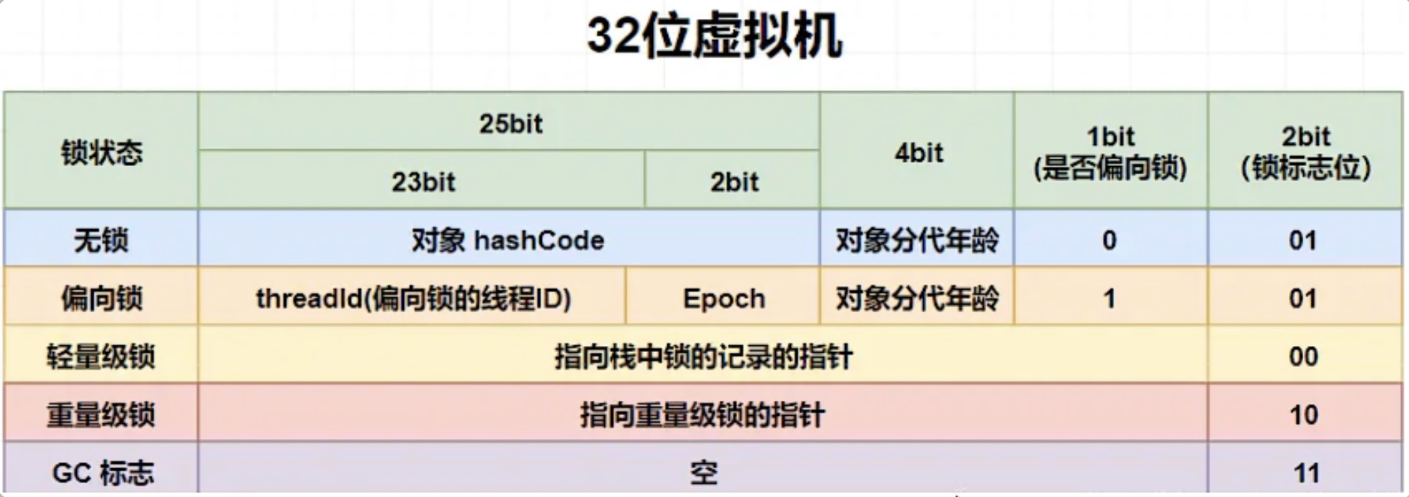
再说对象头的MarkWord
32位
64位


- 看看C中的源码
- oop.hpp

- markOop.hpp
hash:保存对象的哈希码 age: 保存对象的分代年龄 biased_lock: 偏向锁标识位 lock: 锁状态标识位 JavaThread :保存持有偏向锁的线程ID epoch: 保存偏向时间戳
markword(64位)分布图
对象布局、GC回收和后面的锁升级就是对象标记MarkWord里面标志位的变化

聊聊Object obj = new Object()【用代码演示】
JOL证明
JOL工具(Java Object Layout工具)-可以帮助分析对象在Java虚拟机中的大小和布局
http://openjdk.java.net/projects/code-tools/joll(网站已经失效了)
但我们可以直接用依赖来实现这个功能
<dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.jol</groupId>
<artifactId>jol-core</artifactId>
<version>0.9</version>
</dependency><dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.jol</groupId>
<artifactId>jol-core</artifactId>
<version>0.9</version>
</dependency>//简单测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Vm的细节详细情况
System.out.println(VM.current().details());
//# WARNING: Unable to attach Serviceability Agent. You can try again with escalated privileges. Two options: a) use -Djol.tryWithSudo=true to try with sudo; b) echo 0 | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/yama/ptrace_scope
//# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
//# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
//# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
//# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
//# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
//# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
//# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
//# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
//# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
//所有的对象分配的字节都是8的整数倍
System.out.println(VM.current().objectAlignment());
//8
}//简单测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Vm的细节详细情况
System.out.println(VM.current().details());
//# WARNING: Unable to attach Serviceability Agent. You can try again with escalated privileges. Two options: a) use -Djol.tryWithSudo=true to try with sudo; b) echo 0 | sudo tee /proc/sys/kernel/yama/ptrace_scope
//# Running 64-bit HotSpot VM.
//# Using compressed oop with 3-bit shift.
//# Using compressed klass with 3-bit shift.
//# WARNING | Compressed references base/shifts are guessed by the experiment!
//# WARNING | Therefore, computed addresses are just guesses, and ARE NOT RELIABLE.
//# WARNING | Make sure to attach Serviceability Agent to get the reliable addresses.
//# Objects are 8 bytes aligned.
//# Field sizes by type: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
//# Array element sizes: 4, 1, 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 8, 8 [bytes]
//所有的对象分配的字节都是8的整数倍
System.out.println(VM.current().objectAlignment());
//8
}代码
演示一 | 用自带的类
//第一个演示,16bytes演示
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = new Object();//----------新建一个Object对象就是 16bytes
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(o).toPrintable());
}
}
//java.lang.Object object internals:
//----前面8字节时markword
// OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
// 0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
// 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
//----这里的4字节对应的是类元信息
// 8 4 (object header) e5 01 00 f8 (11100101 00000001 00000000 11111000) (-134217243)
//因为必须是8的倍数,这里对齐补充得到16字节
// 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
//Instance size: 16 bytes
//Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total//第一个演示,16bytes演示
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = new Object();//----------新建一个Object对象就是 16bytes
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(o).toPrintable());
}
}
//java.lang.Object object internals:
//----前面8字节时markword
// OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
// 0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
// 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
//----这里的4字节对应的是类元信息
// 8 4 (object header) e5 01 00 f8 (11100101 00000001 00000000 11111000) (-134217243)
//因为必须是8的倍数,这里对齐补充得到16字节
// 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
//Instance size: 16 bytes
//Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total这里丢下一个疑问,为什么类型指针是4字节?之前不都是说是8字节的吗?(因为压缩指针默认开启了)
演示二 | 用自己的类
//只有对象头,没有实例数据,依然是16byte
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer c1 = new Customer();
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(c1).toPrintable());
//com.test.java.Customer object internals:
// OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
// 0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
// 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
// 8 4 (object header) 43 c1 00 f8 (01000011 11000001 00000000 11111000) (-134168253)
// 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
//Instance size: 16 bytes
//Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total
}
}
class Customer{
}//只有对象头,没有实例数据,依然是16byte
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer c1 = new Customer();
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(c1).toPrintable());
//com.test.java.Customer object internals:
// OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
// 0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
// 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
// 8 4 (object header) 43 c1 00 f8 (01000011 11000001 00000000 11111000) (-134168253)
// 12 4 (loss due to the next object alignment)
//Instance size: 16 bytes
//Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total
}
}
class Customer{
}//有了对象头,且有实例数据(int+boolean),它进行了对齐填充,到了24byte
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer c1 = new Customer();
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(c1).toPrintable());
//com.zhang.java.Customer object internals:
// OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
// 0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
// 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
// 8 4 (object header) 43 c1 00 f8 (01000011 11000001 00000000 11111000) (-134168253)
// 12 4 int Customer.id 0
// 16 1 boolean Customer.flag false
// 17 7 (loss due to the next object alignment)
//Instance size: 24 bytes
//Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 7 bytes external = 7 bytes total
}
}
class Customer{
int id;
boolean flag = false;
}//有了对象头,且有实例数据(int+boolean),它进行了对齐填充,到了24byte
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer c1 = new Customer();
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(c1).toPrintable());
//com.zhang.java.Customer object internals:
// OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
// 0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
// 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
// 8 4 (object header) 43 c1 00 f8 (01000011 11000001 00000000 11111000) (-134168253)
// 12 4 int Customer.id 0
// 16 1 boolean Customer.flag false
// 17 7 (loss due to the next object alignment)
//Instance size: 24 bytes
//Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 7 bytes external = 7 bytes total
}
}
class Customer{
int id;
boolean flag = false;
}//有了对象头,且有实例数据(int+boolean),它进行了对齐填充,到了24byte
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer c1 = new Customer();
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(c1).toPrintable());
//com.zhang.java.Customer object internals:
// OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
// 0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
// 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
// 8 4 (object header) 43 c1 00 f8 (01000011 11000001 00000000 11111000) (-134168253)
// 12 4 int Customer.id 0
// 16 1 boolean Customer.flag false
// 17 7 (loss due to the next object alignment)
//Instance size: 24 bytes
//Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 7 bytes external = 7 bytes total
}
}
class Customer{
int id;
boolean flag = false;
}//有了对象头,且有实例数据(int+boolean),它进行了对齐填充,到了24byte
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer c1 = new Customer();
System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(c1).toPrintable());
//com.zhang.java.Customer object internals:
// OFFSET SIZE TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
// 0 4 (object header) 01 00 00 00 (00000001 00000000 00000000 00000000) (1)
// 4 4 (object header) 00 00 00 00 (00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000) (0)
// 8 4 (object header) 43 c1 00 f8 (01000011 11000001 00000000 11111000) (-134168253)
// 12 4 int Customer.id 0
// 16 1 boolean Customer.flag false
// 17 7 (loss due to the next object alignment)
//Instance size: 24 bytes
//Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 7 bytes external = 7 bytes total
}
}
class Customer{
int id;
boolean flag = false;
}GC年龄采用4位bit存储,最大位15
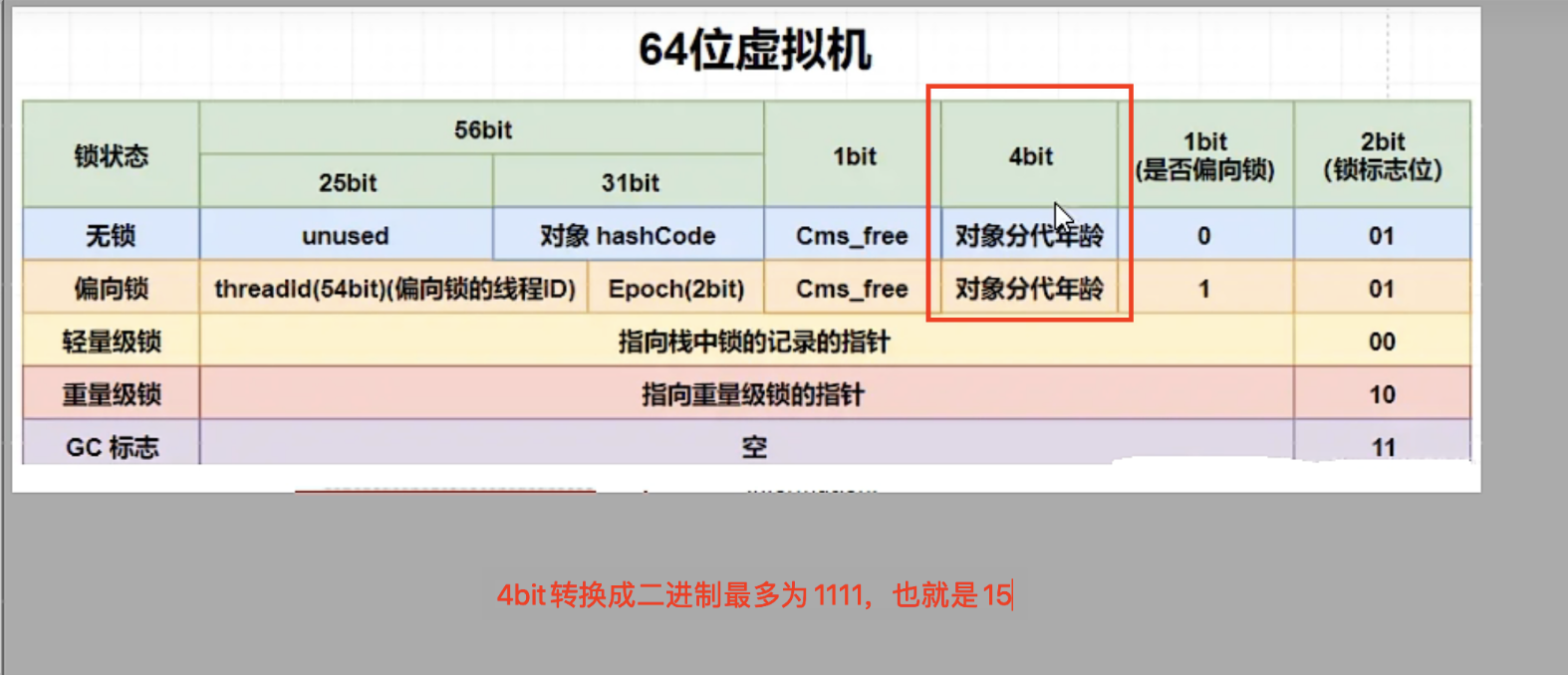
例如MaxTenuringThreshold参数默认值就是15
- 对象分代年龄最大就是15
如果想证明一下
- 我们假如想直接把分代最大年龄修改为16会直接报错。
-XX:MaxTenurningThreshold=16

尾巴参数说明(压缩指针相关)
压缩指针相关的命令(压缩指针是否开启对我们new一个对象是不是16字节的影响)
压缩指针默认是开启的
(这也就解释了为什么前面的类型指针是4个字节,节约了内存空间)

假如不压缩的情况?我们手动关闭压缩指针看看?
+是开启,-就是关闭,所以指令是-XX:-UseCompressedClassPointers
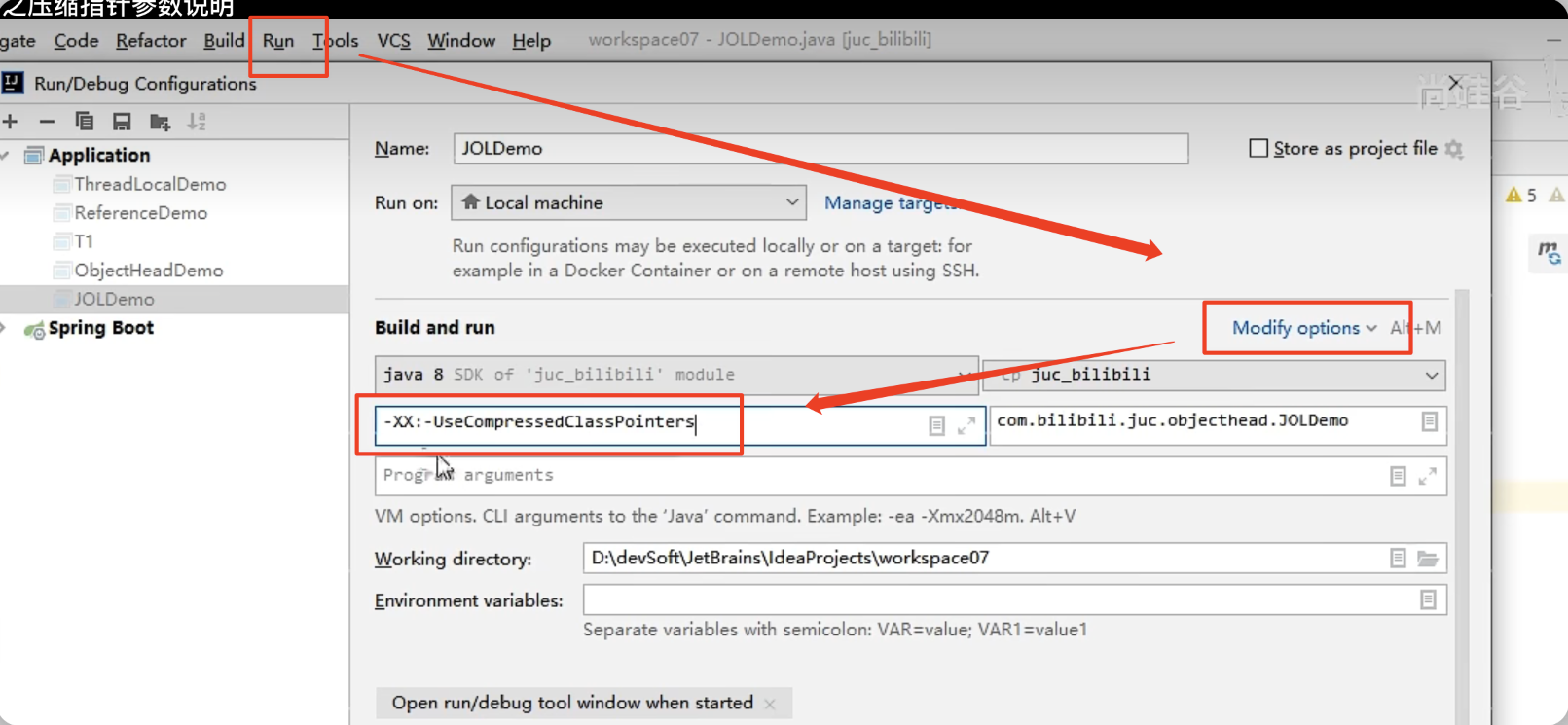
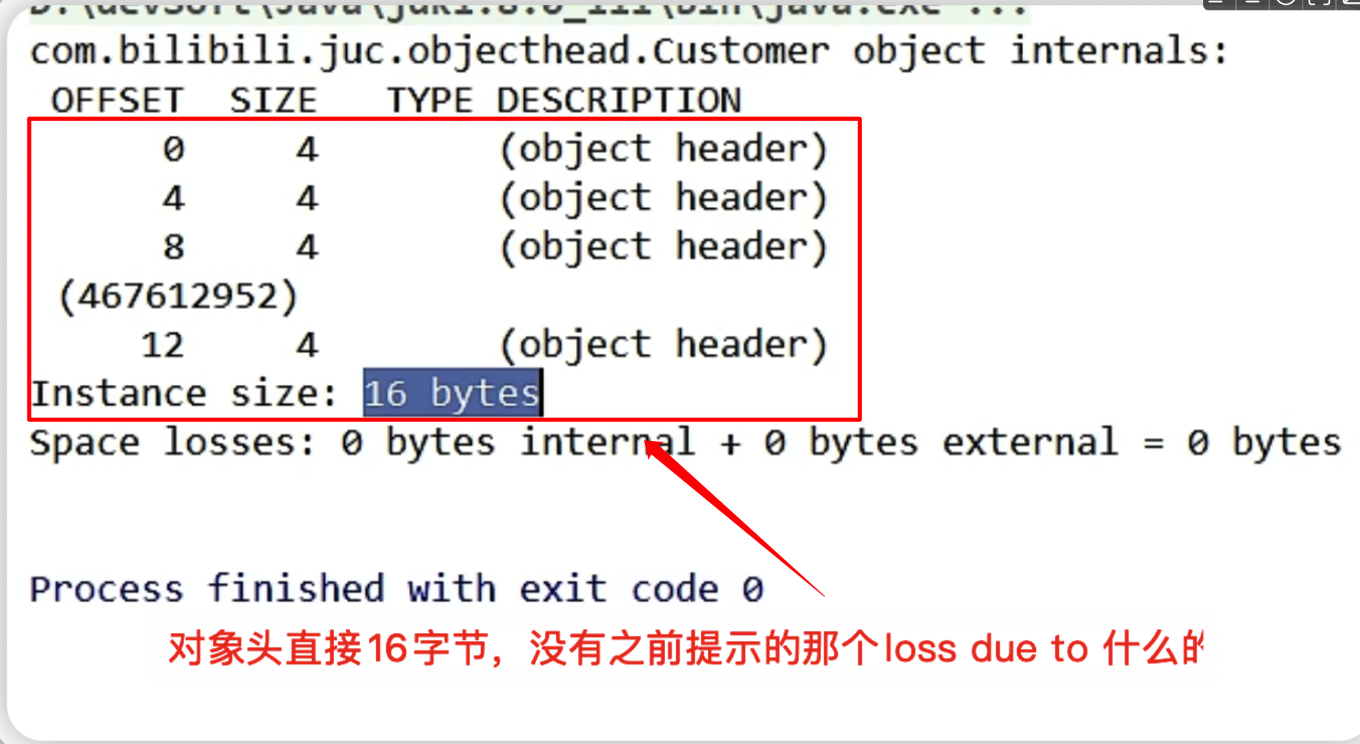
也要注意,不管是否开启压缩指针,创建一个对象就是16字节的。(开启压缩指针后缺失的会由对齐填充补充)
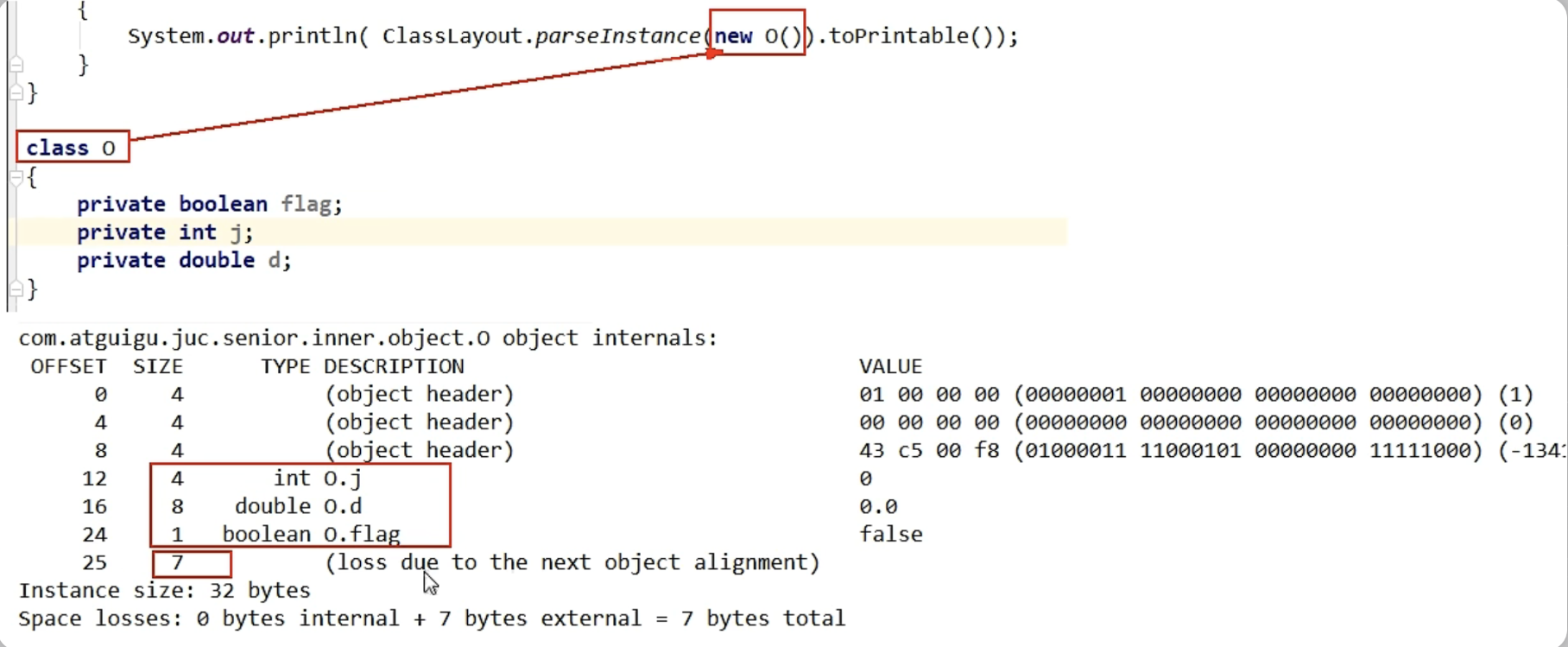
换成其他对象试试
- 同样的道理
 llp-blog
llp-blog