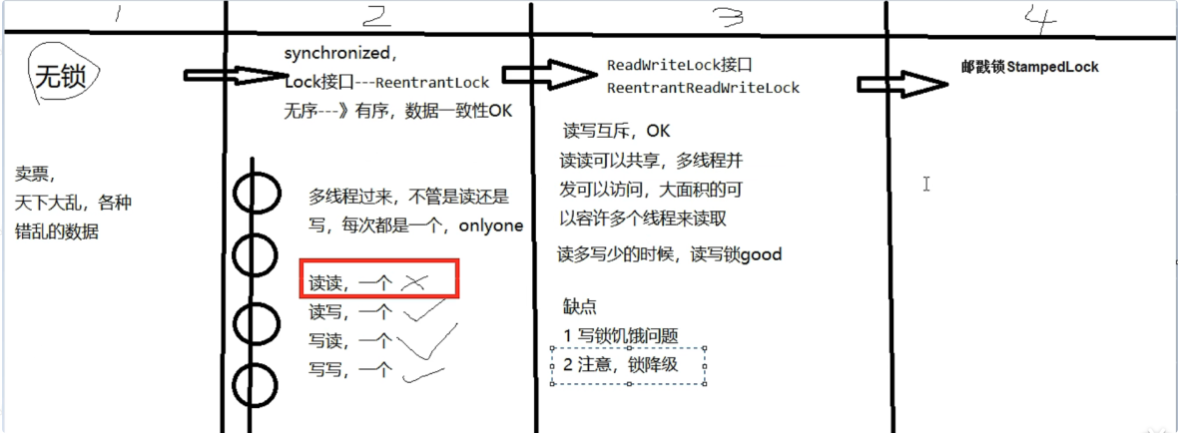
读写锁&&邮戳锁
1.ReentrantReadWriteLock
1.1.读写锁ReentrantReadWriteLock
读写锁:一个资源能够被多个读线程访问,或者被一个写线程访问但是不能同时存在读写线程。
它只允许读读共存,而读写和写写依然是互斥的,大多实际场景是“读/读”线程间并不存在互斥关系,只有"读/写"线程或"写/写"线程间的操作需要互斥的。因此引入ReentrantReadWriteLock 一个ReentrantReadWriteLock同时只能存在一个写锁但是可以存在多个读锁,但不能同时存在写锁和读锁(切菜还是拍蒜选一个)。也即一个资源可以被多个读操作访问―或一个写操作访问,但两者不能同时进行。只有在读多写少情景下,读写锁才具有较高的性能体现。
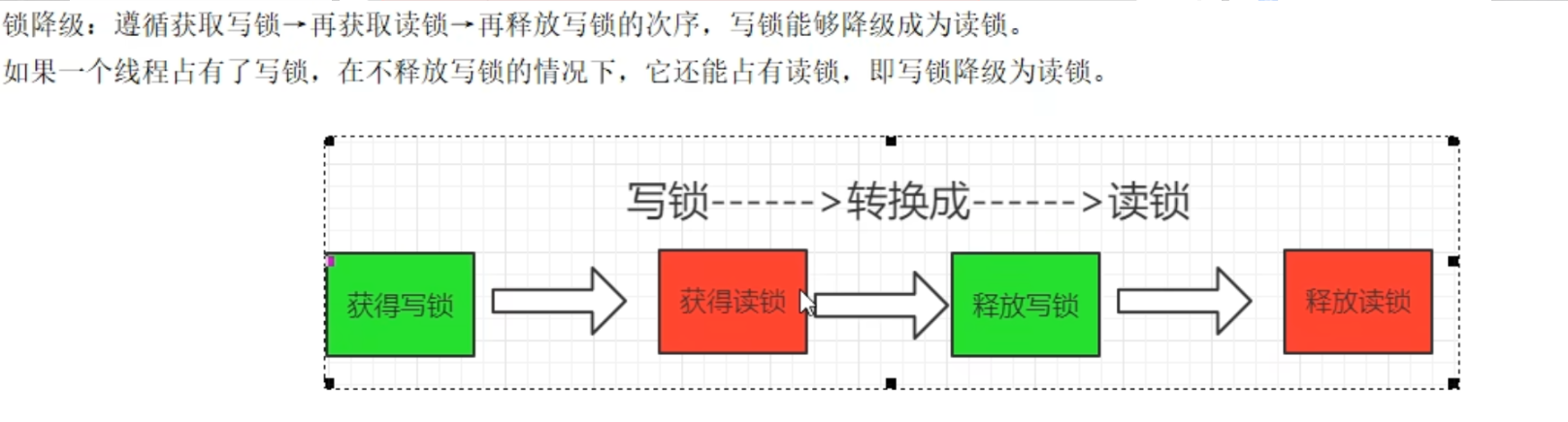
1.2.锁降级

写锁的降级,降级成为了读锁 1)如果同一个线程持有了写锁,在没有释放写锁的情况下,它还可以继续获得读锁。这就是写锁的降级,降级成为了读锁。 2)规则惯例,先获取写锁,然后获取读锁,再释放写锁的次序。 3)如果释放了写锁,那么就完全转换为读锁。
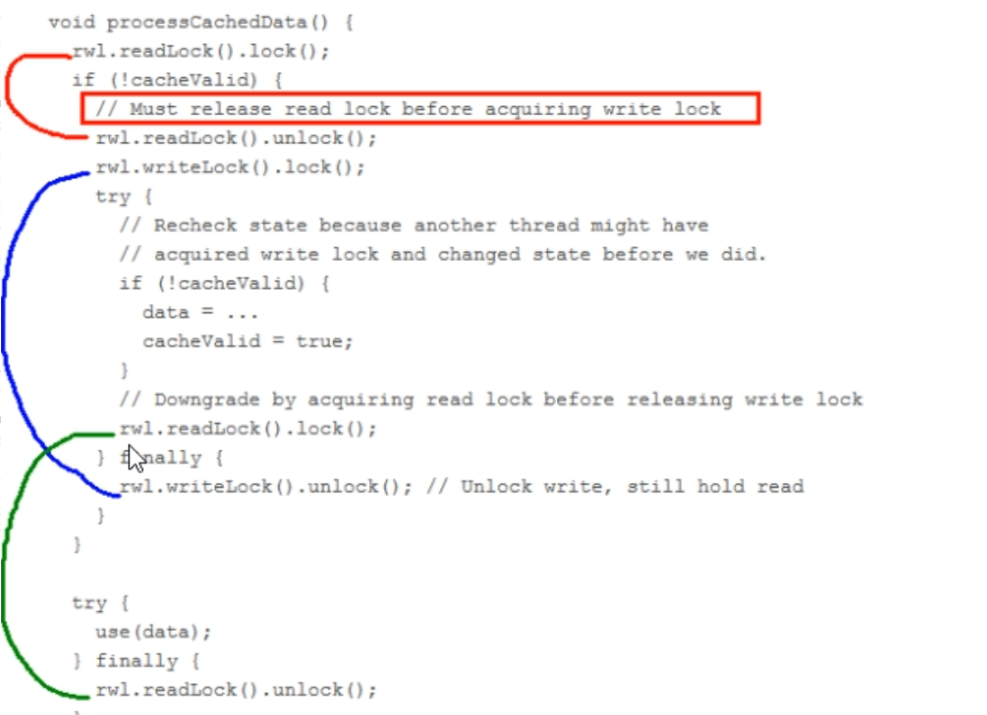
锁降级是为了让当前线程感知到数据的变化,目的是保证数据可见性
如果有线程在读,那么写线程是无法获取写锁的,是悲观锁的策略
在ReentrantReadWriteLock中,当读锁被使用时,如果有线程尝试获取写锁,该写线程会被阻塞。所以,需要释放所有读锁,才可获取写锁。
写锁和读锁是互斥的(这里的互斥是指线程间的互斥,当前线程可以获取到写锁又获取到读锁,但是获取到了读锁不能继续获取写锁),这是因为读写锁要保持写操作的可见性。因为,如果允许读锁在被获取的情况下对写锁的获取,那么正在运行的其他读线程无法感知到当前写线程的操作。
ReentrantReadWriteLock读的过程中不允许写,只有等待线程都释放了读锁,当前线程才能获取写锁,也就是写入必须等待,这是一种悲观的读锁,人家还在读着那,你先别去写,省的数据乱。
分析StampedLock,会发现它改进之处在于: 读的过程中也允许获取写锁介入(相当牛B,读和写两个操作也让你“共享”(注意引号)),这样会导致我们读的数据就可能不一致所以,需要额外的方法来判断读的过程中是否有写入,这是一种乐观的读锁。 显然乐观锁的并发效率更高,但一旦有小概率的写入导致读取的数据不一致,需要能检测出来,再读一遍就行。
1.3.为什么要锁降级?
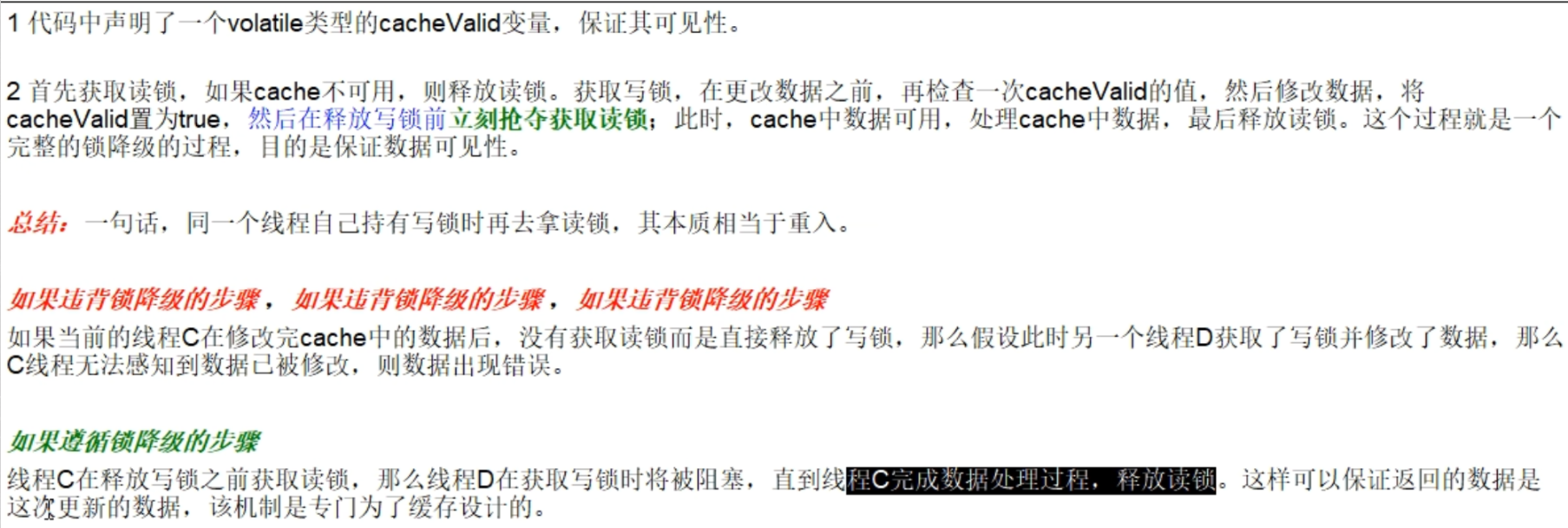
锁降级确实不太贴切,明明是锁切换,在写锁释放前由写锁切换成了读锁。问题的关键其实是为什么要在锁切换前就加上读锁呢?防止释放写锁的瞬间被其他线程拿到写锁然后修改了数据,然后本线程在拿到读锁后读取数据就发生了错乱。但是,我把锁的范围加大一点不就行了吗?在写锁的范围里面完成读锁里面要干的事。缺点呢就是延长了写锁的占用时长,导致性能下降。
1.4.锁饥饿问题
ReentrantReadWriteLock实现了读写分离,但是一旦读操作比较多的时候,想要获取写锁就变得比较困难了,假如当前1000个线程,999个读,1个写,有可能999个读取线程长时间抢到了锁,那1个写线程就悲剧了因为当前有可能会一直存在读锁,而无法获得写锁,根本没机会写。
如何缓解锁饥饿问题? 使用"公平"策略可以一定程度上缓解这个问题,但是"公平"策略是以牺牲系统吞吐量为代价的
StampedLock类的乐观读锁闪亮登场
2.邮戳锁StampedLock
2.1 StampedLock横空出世
StampedLock(也叫票据锁)是JDK1.8中新增的一个读写锁,也是对JDK1.5中的读写锁ReentrantReadWriteLock的优化。
stamp(戳记,long类型) 代表了锁的状态。当stamp返回零时,表示线程获取锁失败。并且,当释放锁或者转换锁的时候,需要传入最初获取的stamp值。
ReentrantReadWriteLock的读锁被占用的时候,其他线程尝试获取写锁的时候会被阻塞。但是,StampedLock采取乐观获取锁后,其他线程尝试获取写锁时不会被阻塞,这其实是对读锁的优化,所以,在获取乐观读锁后,还需要对结果进行校验。
ReentrantReadWriteLock 允许多个线程向时读,但是只允许一个线程写,在线程获取到写锁的时候,其他写操作和读操作都会处于阻塞状态, 读锁和写锁也是互斥的,所以在读的时候是不允许写的,读写锁比传统的synchronized速度要快很多,原因就是在于ReentrantReadWriteLock支持读并发,读读可以共享。
对短的只读代码段,使用乐观模式通常可以减少争用并提高吞吐量
2.2 ReentrantLock、ReentrantReadWriteLock、StampedLock性能比较
package com.bilibili.juc.rwlock;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.StampedLock;
public class ReentrantReadWriteLockTest {
static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
static ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
static StampedLock stampedLock = new StampedLock();
static int read = 1000;
static int write = 3;
static long mills = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
testReentrantLock();
testReentrantReadWriteLock();
// System.out.println("=========================");
testStampedLock();
}
public static void testStampedLock() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
ExecutorService executorServiceWrite = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(read + write);
long l = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < read; i++) {
executorService.execute(() -> {
// tryOptimisticRead();
readStampedLock();
latch.countDown();
});
}
for (int i = 0; i < write; i++) {
executorServiceWrite.execute(() -> {
writeStampedLock();
latch.countDown();
// System.out.println("时间间隔:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-l));
});
}
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executorService.shutdown();
executorServiceWrite.shutdown();
System.out.println("testStampedLock执行耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - l));
}
public static void testReentrantLock() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
ExecutorService executorServiceWrite = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(read + write);
long l = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < read; i++) {
executorService.execute(() -> {
read();
latch.countDown();
});
}
for (int i = 0; i < write; i++) {
executorServiceWrite.execute(() -> {
write();
latch.countDown();
});
}
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executorService.shutdown();
executorServiceWrite.shutdown();
System.out.println("testReentrantLock执行耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - l));
}
public static void testReentrantReadWriteLock() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
ExecutorService executorServiceWrite = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(read + write);
long l = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < read; i++) {
executorService.execute(() -> {
readLock();
latch.countDown();
});
}
for (int i = 0; i < write; i++) {
executorServiceWrite.execute(() -> {
writeLock();
latch.countDown();
// System.out.println("时间间隔:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-l));
});
}
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executorService.shutdown();
executorServiceWrite.shutdown();
System.out.println("testReentrantReadWriteLock执行耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - l));
}
public static void tryOptimisticRead() {
long stamp = stampedLock.tryOptimisticRead();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
if (!stampedLock.validate(stamp)) {
long readLock = stampedLock.readLock();
try {
} finally {
stampedLock.unlock(readLock);
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void readStampedLock() {
long stamp = stampedLock.readLock();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
stampedLock.unlock(stamp);
}
}
public static void writeStampedLock() {
long stamp = stampedLock.writeLock();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
stampedLock.unlock(stamp);
}
}
public static void readLock() {
readWriteLock.readLock().lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
readWriteLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
public static void writeLock() {
readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
public static void read() {
lock.lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void write() {
lock.lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
//输出结果
testReentrantLock执行耗时:15658
testReentrantReadWriteLock执行耗时:265
testStampedLock执行耗时:237package com.bilibili.juc.rwlock;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.StampedLock;
public class ReentrantReadWriteLockTest {
static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
static ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
static StampedLock stampedLock = new StampedLock();
static int read = 1000;
static int write = 3;
static long mills = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
testReentrantLock();
testReentrantReadWriteLock();
// System.out.println("=========================");
testStampedLock();
}
public static void testStampedLock() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
ExecutorService executorServiceWrite = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(read + write);
long l = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < read; i++) {
executorService.execute(() -> {
// tryOptimisticRead();
readStampedLock();
latch.countDown();
});
}
for (int i = 0; i < write; i++) {
executorServiceWrite.execute(() -> {
writeStampedLock();
latch.countDown();
// System.out.println("时间间隔:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-l));
});
}
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executorService.shutdown();
executorServiceWrite.shutdown();
System.out.println("testStampedLock执行耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - l));
}
public static void testReentrantLock() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
ExecutorService executorServiceWrite = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(read + write);
long l = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < read; i++) {
executorService.execute(() -> {
read();
latch.countDown();
});
}
for (int i = 0; i < write; i++) {
executorServiceWrite.execute(() -> {
write();
latch.countDown();
});
}
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executorService.shutdown();
executorServiceWrite.shutdown();
System.out.println("testReentrantLock执行耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - l));
}
public static void testReentrantReadWriteLock() {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
ExecutorService executorServiceWrite = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(read + write);
long l = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < read; i++) {
executorService.execute(() -> {
readLock();
latch.countDown();
});
}
for (int i = 0; i < write; i++) {
executorServiceWrite.execute(() -> {
writeLock();
latch.countDown();
// System.out.println("时间间隔:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-l));
});
}
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executorService.shutdown();
executorServiceWrite.shutdown();
System.out.println("testReentrantReadWriteLock执行耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - l));
}
public static void tryOptimisticRead() {
long stamp = stampedLock.tryOptimisticRead();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
if (!stampedLock.validate(stamp)) {
long readLock = stampedLock.readLock();
try {
} finally {
stampedLock.unlock(readLock);
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void readStampedLock() {
long stamp = stampedLock.readLock();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
stampedLock.unlock(stamp);
}
}
public static void writeStampedLock() {
long stamp = stampedLock.writeLock();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
stampedLock.unlock(stamp);
}
}
public static void readLock() {
readWriteLock.readLock().lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
readWriteLock.readLock().unlock();
}
}
public static void writeLock() {
readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
public static void read() {
lock.lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void write() {
lock.lock();
try {
Thread.sleep(mills);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
//输出结果
testReentrantLock执行耗时:15658
testReentrantReadWriteLock执行耗时:265
testStampedLock执行耗时:237根据执行结果可以明显看出在读多写少的情况下,ReentrantLock的性能是比较差的,而ReentrantReadWriteLock和StampedLock性能差不多相同,而StampedLock主要是为了解决ReentrantReadWriteLock可能出现的锁饥饿问题。
/**
* <p>
* StampedLock = ReentrantReadWriteLock + 读的过程中也允许获取写锁介入
*/
public class StampedLockDemo {
static int number = 37;
static StampedLock stampedLock = new StampedLock();
public void write() {
long stamp = stampedLock.writeLock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "写线程准备修改");
try {
number = number + 13;
} finally {
stampedLock.unlockWrite(stamp);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "写线程结束修改");
}
//悲观读,读没有完成时候写锁无法获得锁
public void read() {
long stamp = stampedLock.readLock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " come in readlock code block,4 seconds continue...");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " 正在读取中......");
}
try {
int result = number;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " 获得成员变量值result:" + result);
System.out.println("写线程没有修改成功,读锁时候写锁无法介入,传统的读写互斥");
} finally {
stampedLock.unlockRead(stamp);
}
}
//乐观读,读的过程中也允许获取写锁介入
public void tryOptimisticRead() {
long stamp = stampedLock.tryOptimisticRead();
int result = number;
//故意间隔4秒钟,很乐观认为读取中没有其它线程修改过number值,具体靠判断
System.out.println("4秒前stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改)" + "\t" + stampedLock.validate(stamp));
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "正在读取... " + i + " 秒" +
"后stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改)" + "\t" + stampedLock.validate(stamp));
}
if (!stampedLock.validate(stamp)) {
System.out.println("有人修改过------有写操作");
stamp = stampedLock.readLock();
try {
System.out.println("从乐观读 升级为 悲观读");
result = number;
System.out.println("重新悲观读后result:" + result);
} finally {
stampedLock.unlockRead(stamp);
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " finally value: " + result);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StampedLockDemo resource = new StampedLockDemo();
/*传统版
new Thread(() -> {
resource.read();
},"readThread").start();
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"----come in");
resource.write();
},"writeThread").start();
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"number:" +number);*/
new Thread(() -> {
resource.tryOptimisticRead();
}, "readThread").start();
//暂停2秒钟线程,读过程可以写介入,演示
//try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
//暂停6秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(6);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "----come in");
resource.write();
}, "writeThread").start();
}
}
//输出结果
4秒前stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改) true
readThread 正在读取... 0 秒后stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改) true
readThread 正在读取... 1 秒后stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改) true
readThread 正在读取... 2 秒后stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改) true
readThread 正在读取... 3 秒后stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改) true
readThread finally value: 37
writeThread ----come in
writeThread 写线程准备修改
writeThread 写线程结束修改/**
* <p>
* StampedLock = ReentrantReadWriteLock + 读的过程中也允许获取写锁介入
*/
public class StampedLockDemo {
static int number = 37;
static StampedLock stampedLock = new StampedLock();
public void write() {
long stamp = stampedLock.writeLock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "写线程准备修改");
try {
number = number + 13;
} finally {
stampedLock.unlockWrite(stamp);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "写线程结束修改");
}
//悲观读,读没有完成时候写锁无法获得锁
public void read() {
long stamp = stampedLock.readLock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " come in readlock code block,4 seconds continue...");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " 正在读取中......");
}
try {
int result = number;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " 获得成员变量值result:" + result);
System.out.println("写线程没有修改成功,读锁时候写锁无法介入,传统的读写互斥");
} finally {
stampedLock.unlockRead(stamp);
}
}
//乐观读,读的过程中也允许获取写锁介入
public void tryOptimisticRead() {
long stamp = stampedLock.tryOptimisticRead();
int result = number;
//故意间隔4秒钟,很乐观认为读取中没有其它线程修改过number值,具体靠判断
System.out.println("4秒前stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改)" + "\t" + stampedLock.validate(stamp));
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "正在读取... " + i + " 秒" +
"后stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改)" + "\t" + stampedLock.validate(stamp));
}
if (!stampedLock.validate(stamp)) {
System.out.println("有人修改过------有写操作");
stamp = stampedLock.readLock();
try {
System.out.println("从乐观读 升级为 悲观读");
result = number;
System.out.println("重新悲观读后result:" + result);
} finally {
stampedLock.unlockRead(stamp);
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + " finally value: " + result);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
StampedLockDemo resource = new StampedLockDemo();
/*传统版
new Thread(() -> {
resource.read();
},"readThread").start();
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"----come in");
resource.write();
},"writeThread").start();
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"number:" +number);*/
new Thread(() -> {
resource.tryOptimisticRead();
}, "readThread").start();
//暂停2秒钟线程,读过程可以写介入,演示
//try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
//暂停6秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(6);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + "----come in");
resource.write();
}, "writeThread").start();
}
}
//输出结果
4秒前stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改) true
readThread 正在读取... 0 秒后stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改) true
readThread 正在读取... 1 秒后stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改) true
readThread 正在读取... 2 秒后stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改) true
readThread 正在读取... 3 秒后stampedLock.validate方法值(true无修改,false有修改) true
readThread finally value: 37
writeThread ----come in
writeThread 写线程准备修改
writeThread 写线程结束修改2.3 StampedLock总结
StampedLock的特点 所有获取锁的方法,都返回一个邮戳( Stamp) , Stamp为零表示获取失败,其余都表示成功; 所有释放锁的方法,都需要一个邮戳(Stamp),这个Stamp必须是和成功获取锁时得到的Stamp一致; StampedLock是不可重入的,危险(如果一个线程已经持有了写锁,再去获取写锁的话就会造成死锁)
StampedLock有三种访问模式 Reading (读模式悲观):功能和ReentrantReadWriteLock的读锁类似 Writing(写模式):功能和ReentrantRedWriteLock的写锁类似 Optimistic reading(乐观读模式):无锁机制,类似于数据库中的乐观锁,支持读写并发,很乐观认对为读取时没人修改,假如被修改再实现升级为悲观读模式
主要API tryOptimisticRead():加乐观读锁 validate(long stamp):校验乐观读锁执行过程中有无写锁搅局
StampedLock的缺点 StampedLock 不支持重入,没有Re开头 StampedLock的悲观读锁和写锁都不支持条件变量(Condition),这个也需要注意。 使用StampedLock一定不要调用中断操作,即不要调用interrupt()方法。
 llp-blog
llp-blog